Millions of people across the globe suffer from hair loss, which has a negative impact on both their self-esteem and their general quality of life. As medical technology improves, hair transplants are now considered a permanent answer. The guide covers the process of hair transplants, the types available, average costs, recovery stage, and some common questions to consider.
Understanding Hair Loss: The Root Cause
It is mainly caused by genes, hormones, aging, or certain health conditions. About half of men over 50 and a third of women suffer from androgenetic alopecia (pattern baldness). Hair transplants help by transferring resistant hair follicles from the back/sides of the head to the areas where hair is thinning.
What is a Hair Transplant?
During a hair transplant, hair follicles are taken from an area with lots of hair and transplanted to bald or thin spots. You get natural results that last, as the hairs transplanted are not affected by balding.
Types of Hair Transplants
1. Follicular Unit Transplantation (FUT)
Procedure: Scalp from the donor area is taken, split into single grafts, and inserted into the bald area.
Pros: A bigger harvest is possible, and it is still cost-effective for extensive plantations.
Cons: Linear scar; longer recovery.
2. Follicular Unit Extraction (FUE)
Procedure: Individual follicles are carefully taken out of the woman's body and then put back into her body in the right place.
Pros: No linear scar; quicker recovery.
Cons: More expensive; time-consuming.
3. Direct Hair Implantation (DHI)
Procedure: Special pens called Choi pens are used to take out and then insert the follicles accurately.
Pros: Natural density; minimal scarring.
Cons: Higher cost; requires skilled surgeons.
4. Robotic Hair Transplants
Procedure: Accuracy in FUE is made possible with the help of ARTAS robot.
Pros: Reduced human error; consistent results.
Cons: Limited availability; expensive.
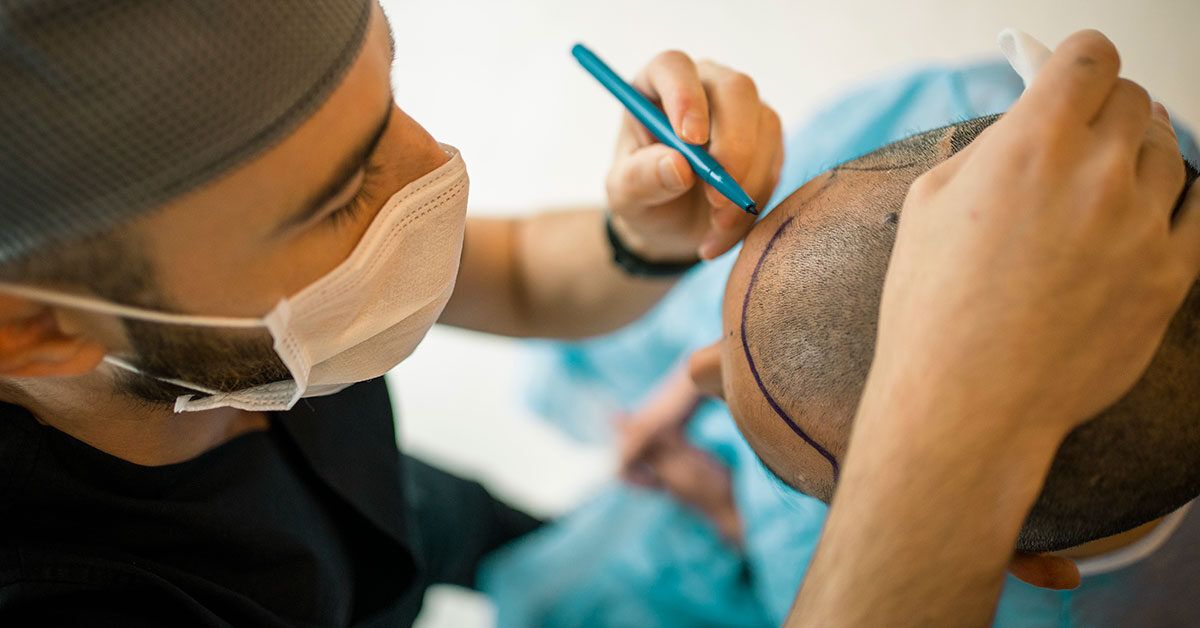
Step-by-Step Hair Transplant Procedure
Consultation: Assess how much hair is being lost, check the area where the new hair will come from, and find out about any relevant medical history.
Design: Plan where the new hair will start, and work out how many grafts you’ll need (usually between 1,500 and 4,000).
Anesthesia: Local anesthesia numbs the scalp.
Extraction: FUT means taking out a strip of skin from the back of your head, while FUE is when each hair is taken out separately.
Graft Preparation: Follicles are sorted under microscopes.
Implantation: Incisions are made in the area of the body receiving the hair, and then the grafts are put in place.
Post-Op Care: Bandages applied; instructions provided.
Who is a Candidate?
Ideal Candidates:
Men/women with androgenetic alopecia.
Sufficient donor hair.
Realistic expectations.
Not Suitable For:
Diffuse thinning (no stable donor area).
Uncontrolled medical conditions (e.g., diabetes).
Pros and Cons of Hair Transplants
Pros:
Permanent results.
Natural appearance.
Boosts confidence.
Recovery and Aftercare Tips
First Week: Avoid getting your new hair too sweaty, touching the grafts after the surgery, or sleeping face-down.
2–4 Weeks: Scabs come off; some of the hairs you get from the donor area can also fall out as the area heals, which is normal.
3–6 Months: New hair growth begins.
Aftercare: Use prescribed shampoos; avoid sun/smoking.
Risks and Side Effects
Temporary swelling, itching, or numbness.
Shock loss (temporary shedding).
Infection or scarring is not common after FUE hair transplants.
Results and Longevity
- Timeline: At around 3–6 months, infants start to change, but full changes are seen by 12–18 months.
- Permanence: Once hair is transplanted, it will last a lifetime, yet medications like finasteride may be needed to stop existing hair from thinning.
Alternatives to Hair Transplants
- Medications: Minoxidil (Rogaine), finasteride (Propecia).
- Low-Level Laser Therapy (LLLT): Stimulates follicles.
- PRP Therapy: Injections boost hair thickness.
FAQs
1. Is a hair transplant painful?
Local anesthesia minimizes discomfort; mild soreness post-surgery.
2. Are results natural?
Yes, modern techniques mimic natural hair patterns.
3. Can women get transplants?
Yes, especially for traction alopecia or thinning crowns.
4. When can I resume work?
Most return within 3–7 days.
Conclusion
Hair transplants can help people with hair loss for a long time, and methods like FUE and DHI make it look natural. While costs and how long it takes to get better can be different for each person, the feeling of getting better and regaining confidence is really important. Consult a certified surgeon to find out what types of treatment might be best for you.